FDA Advisers Endorse Alzheimer’s Drug that Could Slow Disease Progression
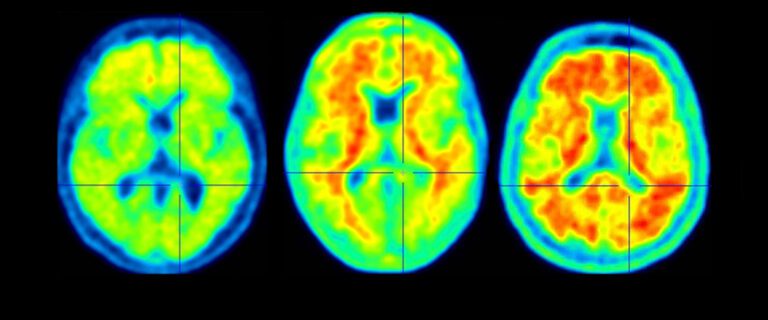
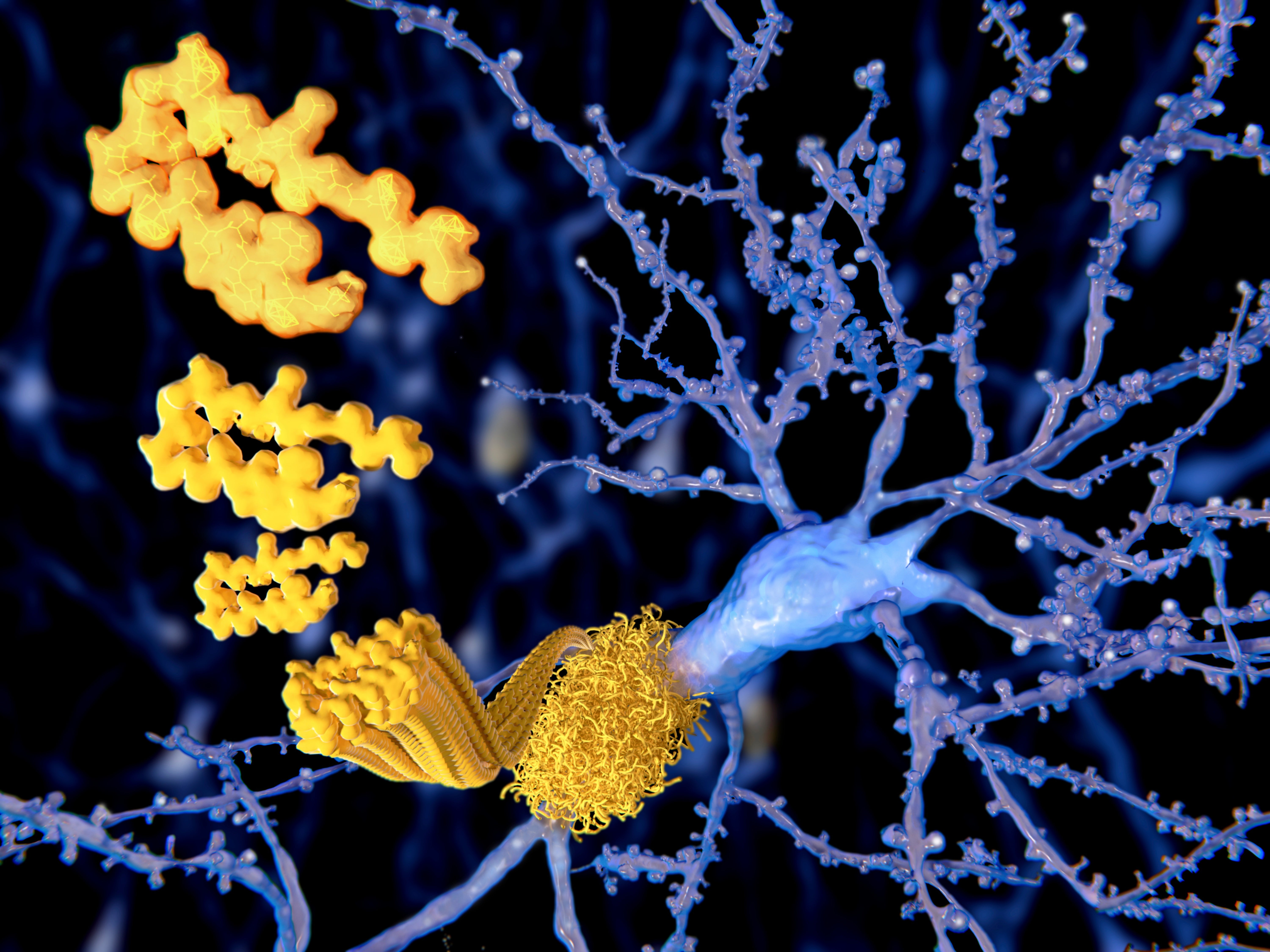
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) advisory committee has voted in favor of recommending approval for a new Alzheimer’s disease drug that could slow the progression of the debilitating brain condition. The drug, aducanumab, was developed by the pharmaceutical company Biogen. It has been shown in clinical trials to reduce the levels of a toxic protein called amyloid beta in the brains of people with Alzheimer’s. Amyloid beta is thought to be a major contributor to the disease’s progression. In a trial published in 2019, aducanumab was shown to slow the rate of cognitive decline by 35% in patients with mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s. The drug also reduced the levels of amyloid beta in the brain by up to 50%. The FDA advisory committee’s vote is a significant step forward for aducanumab. If the FDA approves the drug, it will be the first new Alzheimer’s treatment approved in over two decades. “This is a major development in the fight against Alzheimer’s disease,” said Dr. Lon Schneider, a neurologist at the University of Southern California. “Aducanumab has the potential to slow the progression of the disease and improve the lives of patients and their families.” However, some experts have raised concerns about the safety of aducanumab. In clinical trials, the drug was linked to a rare side effect called ARIA (amyloid-related imaging abnormalities). ARIA can cause swelling and bleeding in the brain. The FDA advisory committee recommended that the FDA require Biogen to conduct further studies to evaluate the safety and efficacy of aducanumab. The FDA is expected to make a final decision on whether to approve aducanumab by June 7, 2021.Alzheimer’s drug that could slow the disease gets support from FDA advisers An experimental Alzheimer’s drug that could potentially slow the progression of the disease has received support from a panel of Food and Drug Administration (FDA) advisers. The drug, lecanemab, is a monoclonal antibody that targets a protein called amyloid beta, which is believed to play a role in the development of Alzheimer’s disease. In a clinical trial, lecanemab was shown to reduce amyloid beta levels in the brain and slow cognitive decline by 27% compared to a placebo. The FDA’s Peripheral and Central Nervous System Drugs Advisory Committee voted 8-1 in favor of recommending that the FDA approve lecanemab for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. The FDA is not bound by the committee’s recommendation, but it often follows the advice of its advisory committees. If approved by the FDA, lecanemab would be the first new Alzheimer’s drug to be approved in nearly 20 years. The current standard of care for Alzheimer’s disease is a class of drugs called cholinesterase inhibitors, which can help to improve symptoms but do not slow the progression of the disease. Lecanemab is not without its risks. In the clinical trial, some patients experienced side effects such as brain swelling and bleeding. However, the committee concluded that the benefits of lecanemab outweigh the risks. The FDA is expected to make a final decision on whether to approve lecanemab by early 2023. If approved, lecanemab would be a major advance in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease and could provide hope for millions of patients and their families.